Previously on History’s Biggest Software Fails, we took the time to explore the World of Warcraft: Corrupted Blood Incidence. While the aforementioned software issue was more of a light-hearted inconvenience, today we take an in-depth look into a security bug that was so severe, that to this day its effects can still be felt:
The Heartbleed Bug
In April 2014 a ripple disrupted the vast waters of the online world as a single bug reigned high over an environment impregnated with mass hysteria. That bug was known as Heartbleed and it left nearly 17% or around 500,000 of the internet’s secure web servers vulnerable to severe breaches of privacy. The Canadian government was forced to take decisive action as 900 social security numbers were stolen. Mumsnet, a UK parenting site, had several accounts hijacked and their CEO impersonated.
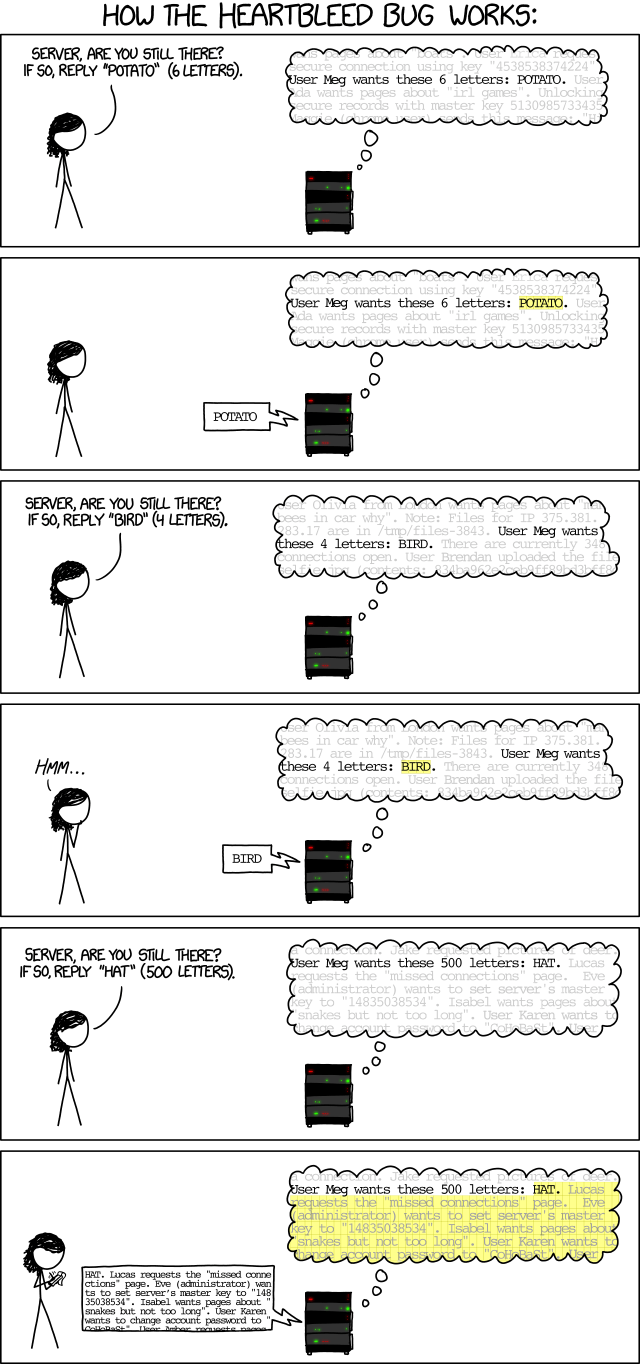
Some of the largest social media sites risked leaking the online population’s most private moments.Heartbleed is a bug that allows a breach in security through exploiting a vulnerability in the Open SSL cryptography library. Improper input validation, which occurs because of a missing bounds check, in the implementation of the Transport Layer Security (TLS) heartbeat extension creates a “buffer-over-read” situation – or the ability for those with ill intentions to access more data than what should be allowed. Simply put:
Explanation of the Heartbleed Bug Soon after word got out, a majority of websites that were suspected to be susceptible to attacks due to Heartbleed began releasing patches to quickly fix the bug. Users all around were strongly encouraged to reset their passwords and the Tor Project of Silkroad infamy advised anyone seeking online anonymity to refrain from using the Internet until things settle and a sense of security is restored. Interestingly, Heartbleed does not only affect websites as certain operating systems such as Android 4.1.1 devices are known to use an outdated version of the OpenSSL library. Worse yet, updating phone software can be a tedious process as a majority of mobiles are controlled by the manufacturers or carriers rather than the creators themselves.There were several repercussions to Heartbleed and the time that companies were forced to invest into developing patches, shutting down their websites and requiring users to change their passwords caused significant negative effects ranging from losses to the necessity of certificate renewals across the World Wide Web.
In fact, the media has often referred to Heartbleed as “the worst vulnerability found (at least in terms of its potential impact) since commercial traffic began to flow on the Internet”. This makes it a true learning experience that highlights the importance of rigorous software testing and makes Heartbleed a strong addition into History’s Biggest Software Fails.